Learning Barriers
Powerful reading, writing, studying and test-taking tools, built on UDL, allowing curriculum to be accessible to all students.
Start with a Free Trial
Kurzweil Education believes that every student can become a steward of their own education when given the right resources and support.
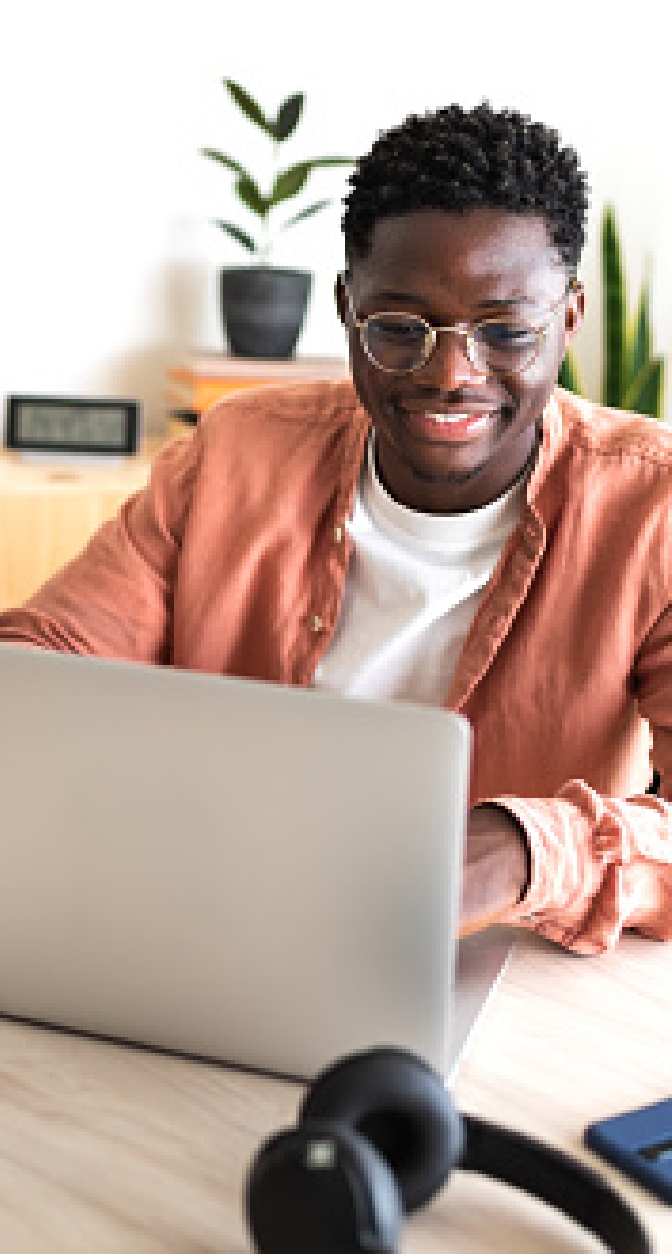



Natural Text-to-Speech voices in 13 languages and 18 additional dialects at customizable reading rates.
Speech-to-Text supports writing and taking notes. Voice notes and dyslexic font add additional support.
Synchronize your Google Classroom students. Create and send assignments.
Use our browser extension to have text read aloud and highlight text on the web to export into a study guide within Kurzweil 3000.
Guide and assess reading comprehension with interactive bubble notes.
Highlight, circle and strikethrough to emphasize the critical pieces of your text.
Access your content from Google Drive, OneDrive, Bookshare, along with over 1800 classic texts in our Universal Library.
Improve test performance with numerous study tools including column notes, annotations, dictionaries and translation.
Provide Single Sign On through Google, Microsoft, ClassLink or SAML.
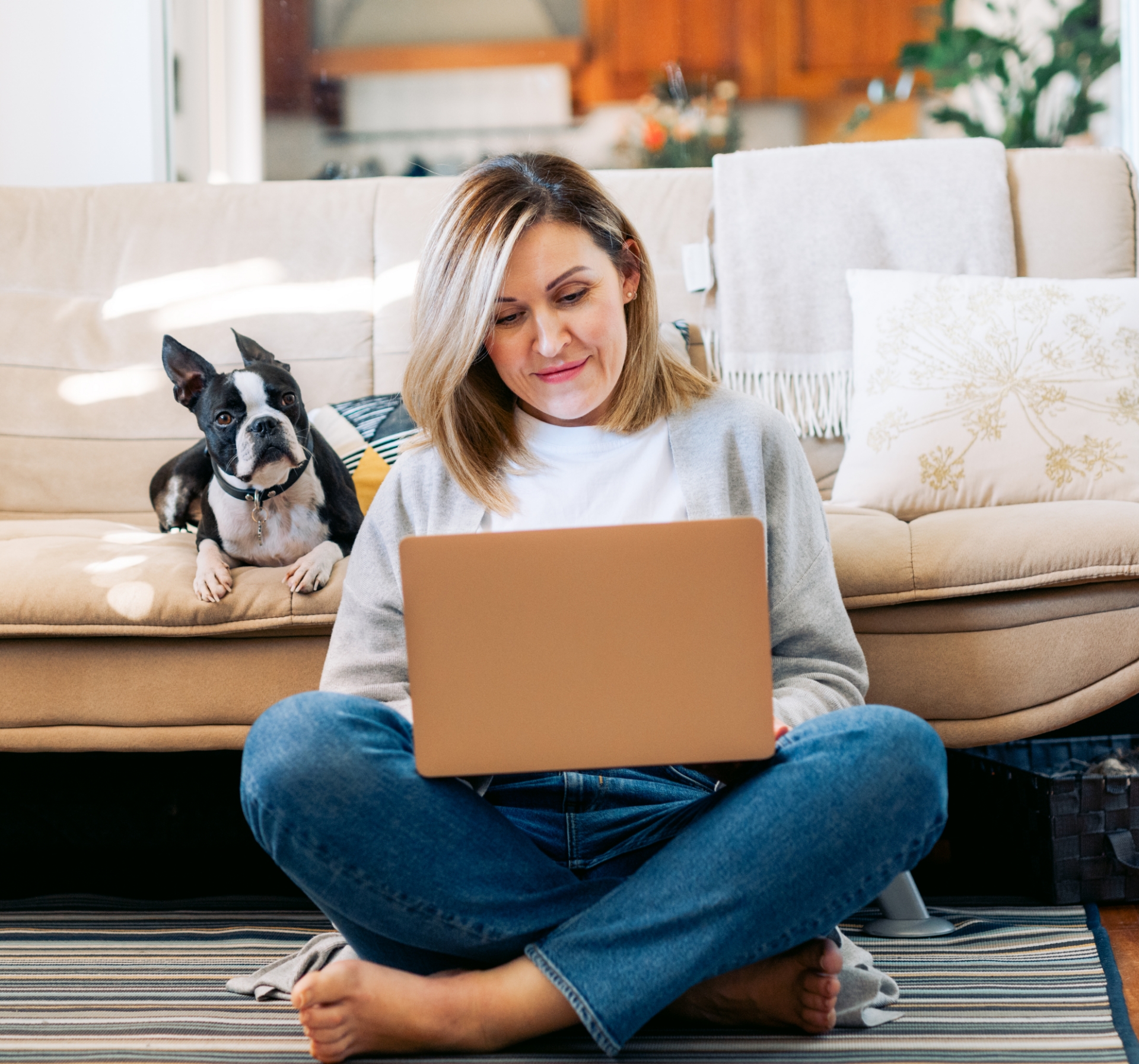






Kurzweil Education is independent learning at it's best! Watch our video to learn more about how to take control of your education.